- support@ddgear.com
- North 3F, Building 13-2, Zhixin Park, NO.1099 Xianhua South Street, Wucheng, Jinhua, Zhejiang, China.
Products
Intermediate Drive Shaft Assembly – Precision for EV | DD Gear
Product Details
FAQ
Features & Benefits
-
Stable torque transfer between e-axle and wheel
The intermediate drive shaft assembly transmits torque from the EV gearbox or differential to the CV axle, acting as the mechanical link between drivetrain output and the wheel. -
Improved handling and reduced torque steer
By creating equal or controlled-length half shafts, the intermediate shaft helps keep inner joint angles similar on both sides of the vehicle, which reduces torque steer and contributes to stable straight-line driving under high motor torque. -
High strength and fatigue resistance
Shaft geometry, material selection, and heat treatment are tuned for high torque and repeated loading from acceleration, regenerative braking, and rough road conditions, with attention to spline root strength and journal fillets. -
Precision-machined splines and bearing journals
Splined ends, circlip grooves, and bearing journals are machined and ground to tight tolerances for accurate fit and easy assembly with CV joints, bearings, and brackets, supporting smooth rotation and long component life. -
Integrated support bearing and bracket interface
The intermediate drive shaft assembly can be supplied with bearing seats and housing interfaces designed for your bracket, helping maintain alignment between gearbox and half shaft under vehicle vibration and thermal expansion. -
Designed for compact EV packaging
Shaft length, diameter, and bracket position are optimised to fit within tight EV underbody and motor-bay packaging, coordinating with e-axle housing, suspension geometry, and wheel offset. -
From prototypes to series production
DD Gear can provide rapid prototypes for vehicle dynamics and durability testing and then transition to controlled series production with stable quality and documentation.
Technical Specifications
Final data will be defined according to the customer’s drawing and EV duty cycle.
| Item | Typical Option |
| Gear Type | Solid or tubular steel shaft with splines on one or both ends |
| Pressure Angle | 20° (other angles according to OEM standard) |
| Material | Alloy steels suitable for induction hardening or Q&T (e.g. 40Cr, 42CrMo equivalents, other automotive-grade steels |
| Heat Treatment |
Induction hardening on splines/journals, quench-and-temper, or other processes defined by fatigue and wear requirements |
| Surface Hardness | Typically 50–60 HRC or per drawing |
Applications
-
Front-drive EVs and hybrid vehicles
Intermediate shafts between the transaxle output and one of the front half shafts, used to equalize left/right drive shaft lengths and improve ride and handling at high motor torque. -
Integrated e-axles with offset motor positions
Shafts that connect offset motors or gearsets to the wheel-side CV axles in compact drive units, accommodating packaging constraints while maintaining desired shaft angles. -
Electric light trucks and vans
Intermediate shaft assemblies used in vehicles with long half-shaft spans or non-symmetric layouts where a separate support bearing is needed for durability. -
All-wheel-drive EV variants
Intermediate shafts used in front or rear drivelines where multiple axles or e-axles share torque and equal-length driveshafts are needed to control vehicle response.
Gear Manufacturing Process

Every intermediate drive shaft assembly is produced under a controlled manufacturing route designed for precision and durability. A typical process flow is:
-
Forging or bar cutting of shaft blanks
-
Lathe machining of diameters, bearing journals, and reference surfaces
-
Milling, drilling, and spline cutting operations
-
Additional CNC machining as required by geometry
-
Heat treatment (such as quenching and tempering, induction hardening)
-
Shot blasting and stress relief as required
-
Finish machining and grinding of critical mounting surfaces and journals
-
Cleaning and rust prevention treatment
-
Final inspection and packaging for shipment
Precision Gear Customization Process
To support custom intermediate drive shaft assembly projects, DD Gear follows a clear, eight-step customization process:
Step 1 – Requirement Collection
Customers provide design requirements, 2D drawings, 3D models, or physical samples, together with basic duty cycle information (torque, speed, life, installation).
Step 2 – Drawing Design & Optimization
Based on the provided drawings or samples, DD Gear prepares or optimizes detailed manufacturing drawings and shares them with the customer for confirmation.
Step 3 – Quotation
After the drawings and technical points are confirmed, we issue a precise quotation covering tooling, piece price, lead time, and quality requirements.
Step 4 – Tooling & Fixture Preparation
Once the price is confirmed, we arrange tooling and fixture production. Any tooling cost is agreed with the customer in advance and can be offset or refunded after mass orders, according to the commercial agreement.
Step 5 – First Sample Approval
After tooling and fixtures are ready, we manufacture the first sample batch—typically within about 30 days—and ship it to the customer for testing.The customer inspects and validates the samples in their gearbox or test bench and provides feedback on dimensions, performance, and any required adjustments.
Step 6 – Mass Production
When the sample is approved, we start mass production according to the agreed production plan and quality standards.
Step 7 – Finished Product Inspection
After production, we inspect hardness, dimensions, runout, tooth accuracy, and other critical characteristics to ensure full compliance with the drawing and standards.
Step 8 – Shipping Arrangement
Once inspection is passed and shipment is approved by the customer, we arrange booking, packaging, and delivery to the specified destination.
Quality Assurance & Inspection
DD Gear applies the same quality philosophy to all precision gears:
-
Quality management systems based on ISO 9001 and IATF 16949
-
Process control from incoming material to final inspection, including:
-
Material certification and chemical composition checks
-
Hardness and case depth verification after heat treatment
-
Gear measurement for profile, lead, pitch, and runout
-
Surface roughness testing on gear flanks and journals
-
Dimensional inspection with calibrated gauges and CMMs
-
-
Traceability for each batch with inspection records and reports
- Optional documentation such as PPAP/FAIR packs on request
Packaging

Usage & Installation Notes
-
Ensure correct installation of the support bearing and bracket to maintain shaft alignment relative to the gearbox and half shafts.
-
Confirm that spline engagement depth and circlip retention meet design specifications to avoid disengagement under load.
-
Use specified torque values for bracket and flange fasteners; incorrect torque may lead to noise, vibration, or premature wear.
-
Verify that left and right half-shaft lengths and joint angles match the intended design, especially after any layout changes or service work.
-
Use the recommended gearbox or e-axle lubricant and maintain oil level and cleanliness.
-
During service, inspect splines, bearing seats, and coating surfaces for corrosion, scoring, or wear, particularly in regions exposed to road splash and salt.
-
Store finished parts in dry, clean conditions with anti-rust protection and avoid impacts on splines and journals.
Company Strength – DD Gear
-
Specialized in small module, high-precision gears and shafts for EVs, humanoid robots, AGVs, and intelligent automation.
-
Integrated manufacturing from forging and machining to heat treatment and gear grinding.
-
Quality systems aligned with automotive standards, with experience supporting OEM and Tier 1 projects.
-
Engineering support covering concept feasibility, DFM reviews, and failure analysis feedback.
-
Global export capability with experience serving customers in multiple countries.
Q1: What information do you need for an intermediate drive shaft assembly quotation?
We normally need 2D drawings (PDF), 3D models (STEP/IGES if available), material and heat treatment requirements, expected annual volume, and basic application data such as vehicle type, torque, shaft layout, and life targets.
Q2: Can you help tune shaft length and layout to reduce torque steer?
Yes. Our engineering team can coordinate with your chassis and drivetrain layout to help define intermediate shaft length and stiffness that support equal or controlled half-shaft lengths and improved straight-line behaviour, while still fitting within packaging limits.
Q3: What lead time should we expect for prototypes and production?
Prototype intermediate drive shaft assemblies are usually available in around 2–3 weeks after final drawing confirmation and tooling readiness. Mass production lead time depends on quantity and process route and will be confirmed during quotation.
Q4: Do you supply the complete CV axle or only the intermediate shaft?
DD Gear mainly focuses on precision shafts, gears, and related components. We typically supply the intermediate drive shaft and associated machined features; complete CV axle assemblies are usually handled by specialized axle or system suppliers.
Q5: What materials and heat treatments can you provide?
We work with a range of alloy steels suitable for induction hardening and quench-and-temper processes. Material grade and heat treatment are defined according to torque, stiffness, and fatigue requirements for your EV platform.
Q6: What is your typical MOQ for intermediate drive shaft assemblies?
MOQ depends on the complexity of the part and tooling. We support flexible MOQ for development and pilot builds, then align batch sizes with your series production plan.
Q7: Can you provide inspection reports with each batch?
Yes. Dimensional inspection reports, hardness records, and other documents can be provided according to your requirements.
Reliable precision gears for robotics, automotive, and beyond.

Custom Gears for Sliding, Swing & Industrial Doors | DD Gear
Automatic Door Gear from DD Gear is a range of custom-designed, small- to medium-module gears and shafts used in automatic sliding doors, swing doors, revolving doors and industrial doors (sectional, rolling, high-speed doors). In these systems, compact electric motors drive gearboxes and gear trains that must deliver high starting torque, smooth motion and very low noise while opening and closing heavy door leaves hundreds or thousands of times per day. Typical automatic door operators use one or more stages of spur and helical gears in combination with worm gears or bevel gears. Spur gears provide simple, efficient torque transfer for intermediate stages. Helical gears, with their angled teeth and higher contact ratio, help achieve quieter and smoother running, which is critical in hotels, hospitals, offices and residential buildings. Worm gears are often used for high reduction ratios and self-locking behavior, improving safety when the door is at rest and reducing backdrive from wind loads or manual pushing. In some operators, bevel gears change shaft direction between the motor, transmission and drive shaft or belt/chain. DD Gear manufactures Automatic Door Gears strictly on a custom, build-to-print basis. Using customer drawings or validated samples, we supply spur and helical pinions and gears, worm gears and worm wheels, bevel gears, gear shafts and related components for door operators. Through appropriate alloy steels, surface treatments, controlled heat treatment and precision machining, DD Gear helps door-operator OEMs and system integrators build drives that provide quiet operation, long life and reliable performance in entrances exposed to dust, temperature changes and frequent cycling.
Custom Precision Gears for Electric Wheelchair | DD Gear
Electric Wheelchair Gear from DD Gear covers a family of small-module, custom-designed gears and shafts used in electric wheelchairs, powered mobility scooters and related assistive devices. In these products, compact electric motors drive wheel-side or centrally mounted gearboxes that must deliver high torque at very low vehicle speed, provide smooth, gentle acceleration and braking, and work reliably for years in both indoor and outdoor environments. Typical electric wheelchairs use a single-speed reduction between the high-speed motor and the drive wheel. This reduction is often realized by a worm gear stage, a spur/helical reduction stage, or a planetary gear set integrated into a wheel-side gearbox. Worm gears are commonly used because they can offer high reduction ratios and inherent self-locking behavior in many designs, helping the chair hold position on slopes when the motor is not powered. Spur and helical gears are used in intermediate stages or in designs where efficiency and low noise are prioritized. Planetary gear trains may be used when high torque density and compact packaging are critical, especially in wheel modules. DD Gear manufactures Electric Wheelchair Gears strictly on a custom, build-to-print basis. Based on customer drawings or validated samples, we supply worm gears and worm wheels, spur and helical gears, planetary gear components (sun, planet, ring), gear shafts and wheel-drive gear elements. Using case-hardening steels, controlled heat treatment and small-module precision machining or grinding, DD Gear helps mobility OEMs and system suppliers design drivetrains that offer quiet operation, safe holding behavior, good efficiency and long service life, enhancing comfort and confidence for end users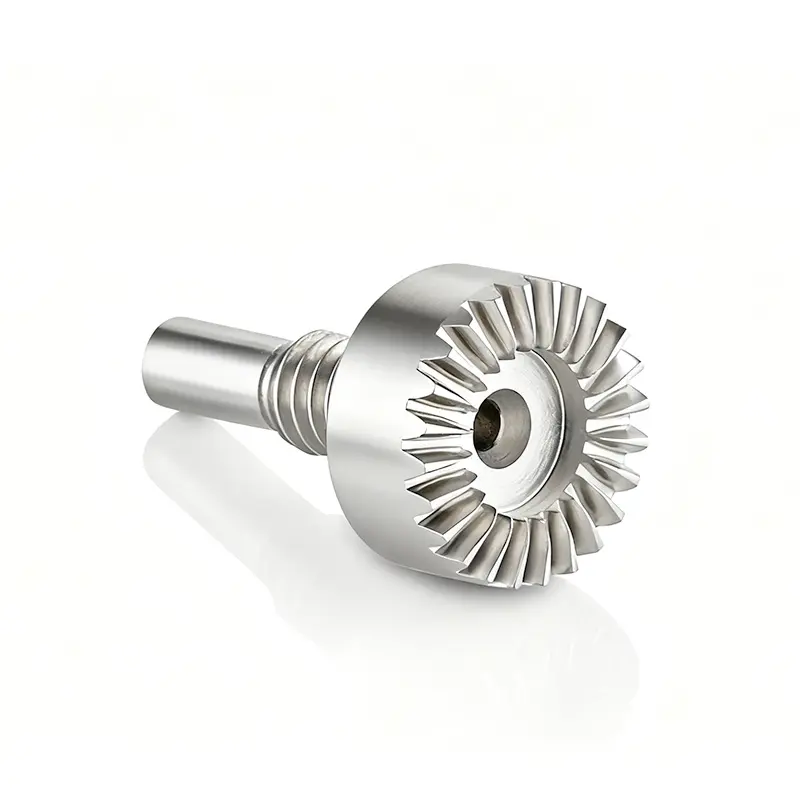
Custom Precision Gears for Surgical Robotics | DD Gear
Surgical Robot Gear from DD Gear covers a family of small-module, high-precision gears and shafts used in surgical robots, robotic-assisted surgical systems and related medical robotic platforms. In these applications, compact actuators drive robotic arms, wrists, end effectors and instrument modules that must deliver micron-level positioning, smooth motion and highly repeatable force control, often in minimally invasive procedures around critical anatomy. To achieve this, surgical robots commonly use spur and helical gears, planetary gear sets and gears integrated with harmonic or other precision reducers inside joint and instrument actuators. These gear stages must work with high-resolution encoders and advanced control algorithms, providing low backlash, high torsional stiffness and consistent friction characteristics across the full range of motion. At the same time, many components operate near the sterile field and must tolerate frequent cleaning and sterilization cycles, use biocompatible or low-outgassing materials and lubricants, and minimize particle generation. DD Gear manufactures Surgical Robot Gears strictly on a custom, build-to-print basis. Based on your drawings or validated samples, we supply spur, helical and bevel gears, planetary components (sun/planet/ring), gear shafts, small-module pinions and interface gears for precision reducers, using carefully selected alloy steels, stainless steels and, where specified, non-magnetic or corrosion-resistant materials. With controlled heat treatment, precision machining and (when required) ground tooth flanks, DD Gear supports surgical robot OEMs and system suppliers in building actuators that deliver precise, smooth and reliable motion, while supporting cleaning and sterilization concepts defined at the system level.
Custom Precision Gears for Automated Guided Vehicles | DD Gear
AGV Gear from DD Gear refers to a range of custom, small-module gears and shafts specifically engineered for Automated Guided Vehicles (AGV) and Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR) used in warehouses, factories, distribution centers and logistics hubs. In these applications, compact electric motors drive wheel-mounted or centrally mounted gearboxes that must deliver high torque at low travel speed, provide smooth, precise motion control, and withstand continuous start/stop cycles in 24/7 intralogistics operations. Typical AGV drivetrains combine motor + reduction gearbox + drive wheel, often in a wheel hub or wheel-side gearbox design, while steering and lifting functions may use additional gear stages or screw drives. Single- or multi-stage spur and helical gears are common in wheel drives and intermediate stages, while planetary gear sets are widely used where high torque density and compact packaging are required, such as in drive wheels for heavy loads or AGV forklifts. In some architectures, gears are also combined with chain or belt stages to reach the final wheel or mast. Compared with traditional industrial vehicles, AGV/AMR systems place greater emphasis on low noise, smooth operation, positioning accuracy and long maintenance intervals. DD Gear manufactures AGV gears strictly on a custom, build-to-print basis, supplying spur and helical gears, planetary gear components (sun/planet/ring), bevel gears, gear shafts and wheel-drive gear elements based on customer drawings or validated samples. Using case-hardening steels, controlled heat treatment and small-module precision machining or grinding, DD Gear supports AGV and AMR OEMs in building transmissions that provide high efficiency, compact size, low NVH and long service life in demanding indoor and outdoor logistics environments.
Custom Reduction Gears & Shafts for E-Motorcycle | DD Gear
E-Motorcycle Gear from DD Gear refers to a range of small-module reduction gears and shafts engineered for electric motorcycles, e-scooters, e-mopeds and high-power e-bikes. Instead of multi-speed gearboxes like those used in traditional ICE motorcycles, most electric two-wheelers use a single-speed reduction between the high-speed electric motor and the wheel. This reduction can be realized by hub-motor planetary gear sets, mid-drive spur/helical gear stages, or a combination of gear reduction + chain or belt drive. In hub-motor architectures, a compact planetary gear train is often integrated inside the wheel hub to reduce motor speed and increase wheel torque while keeping unsprung mass and noise under control. In mid-drive or centrally mounted motor layouts, the motor drives an intermediate shaft via spur or helical gears, and torque is then transferred to the rear wheel by a chain or belt. In both cases, the gears must handle high input speeds, frequent acceleration/deceleration, high torque at low road speed, outdoor exposure and strict NVH requirements, all within tight packaging envelopes. DD Gear manufactures E-Motorcycle Gears strictly on a custom, build-to-print basis. Using customer drawings or validated samples, we supply spur and helical pinions and gears, planetary gears (sun/planet/ring), gear shafts and hub-motor gear components. With appropriate case-hardening steels, controlled heat treatment and small-module precision machining or grinding, DD Gear helps electric two-wheeler OEMs and system suppliers build drivetrains that deliver high efficiency, quiet operation, compact packaging and long service life, supporting both urban commuting and higher-performance applications
Custom Precision Gears for Packaging Machinery | DD Gear
Packaging Machinery Gear from DD Gear is a family of small- to medium-module, custom-designed gears used in form-fill-seal (FFS) machines, cartoners, case packers, palletizers, labelers and conveyor systems. In modern packaging lines, gears are responsible for coordinating motion between film feed, sealing jaws, product infeed, carton erection, filling, closing and outfeed. They must operate at high speed, often in 24/7 duty, while maintaining precise timing and position to avoid film waste, misaligned seals, product jams and unplanned downtime. Most packaging mechanisms rely on spur and helical gears in gearboxes and timing stages for parallel shafts. Spur gears provide simple, highly efficient torque transmission and are widely used in indexing, feed and cam drives. Helical gears, with their angled teeth and higher contact ratio, offer smoother, quieter running and higher load capacity, which is important in high-speed packaging halls where noise and vibration affect both productivity and operator comfort. In right-angle or compact layouts, bevel gears, worm gears or planetary sets may be used to change direction or achieve higher reduction ratios in a limited envelope. DD Gear manufactures Packaging Machinery Gears strictly on a custom, build-to-print basis. Based on your drawings or validated samples, we supply precision spur, helical, bevel gears, gear shafts and internal gears, using case-hardening steels, nitriding steels, stainless or corrosion-resistant grades, and selected engineering plastics where appropriate. Through controlled heat treatment, finishing and systematic quality control, we help packaging OEMs and retrofitters build gear trains that deliver stable speed ratios, smooth motion, low noise and long service life, even in demanding environments involving dust, humidity or washdownExploring The Science of Precision Gears
How Gear Design, Materials, and Standards Shape Performance
In the intense world of industrial automation, the gap between a machine that runs smoothly and one that breaks down badly often rests on the tiny precision of its gears. Current uses, like electric vehicle (EV) motors turning at 15,000+ RPM or robotic arms needing sub-micron positioning accuracy, put heavy demands on drivetrain parts. When regular stock items fall short of the needs for noise, vibration, and lasting strength, tailored precision work turns into the main choice. At DD Gear, we have focused for over 15 years on made-to-order, build-to-print precision gear manufacturing, supplying big makers worldwide in fields from humanoid robotics to electric passenger vehicles. Our goal stays firm: deliver gears that mix accuracy, toughness, and quiet running to push forward smart motion. Gear Design: Optimizing Geometry for Performance The shape of a gear sets how power moves and how the setup handles stress. For fast spins and strong twists, the planning stage matters a lot to cut down noise and stretch out working life. Tooth Profile and Engagement: Spur vs. Helical Picking the best tooth shape starts the whole gear design process: Spur Gears: Have straight teeth lined up with the axis. They work well (94–99%) and cost less for shafts that run side by side, but they can make a bump sound at quick speeds from quick tooth hits. Helical Gears: Have teeth sliced at a slant, which lets one tooth grab on before the last one lets go. This leads to much quieter work and bigger load handling, so custom helical gears stand as the usual pick for EV gearboxes and quick automation. Micro-geometry Tweaks for NVH Control To cut back more on Noise, Vibration, and Harshness (NVH), workers add certain changes to the tooth face: Crowning: Shaping the tooth surface so contact stays in the middle even when shafts bend under big twists. Tip Relief and Lead Correction: Taking off small bits at the tooth ends or tips to stop bangs and share forces evenly. Flank Polishing: A smoothed and shined tooth side drops friction waste, boosting drivetrain work by up to 1.2%. Compact High-Ratio Configurations Today’s robotics and Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) call for big drop ratios in small spots: Planetary Gear Sets: These give strong torque in a tight area by sharing the load over several planet gears, perfect for robot arms and AGV drive wheels. Harmonic Reducers: For custom robotic joints, these bring high-ratio drops (up to 320:1) with almost no play in a small, straight-line setup. Materials and Heat Treatment: The Science of Durability A gear tooth deals with huge bending pull at its base and smashing push at the contact line. Choosing the right metal mix and hardening method marks the difference between a gear that holds up one year and one that goes five. Specialized Case-Hardening Steels Top-performing gear groups often begin as shaped pieces of strong alloy steels: 18CrNiMo7-6 and 20MnCr5: These are used a lot in heavy-load custom helical gears because of their solid fight against wear-out and inner strength. 20CrMnTi: A common choice for CNC machine gears and power tools, giving a mix of wear resistance and hit toughness. Non-Magnetic Options: For medical scan gear, like drives near MRI tables, custom answers use aluminum bronze or austenitic stainless steels to keep things safe and clear in images. The Carburizing Advantage Carburizing adds carbon to the outer skin of the steel in a heat step: Dual-Property Structure: It builds a tough outer layer (58–62 HRC) to battle wear, while keeping a softer, stronger core (35–45 HRC) to take in quick hits without breaks. Consistency: At DD Gear, a tightly-managed process holds case depth in a 0.05 mm band, ensuring steady results over many units. For deeper facts on metal traits in gear making, check the American Gear Manufacturers Association (AGMA) for trusted rules known around the world. Standards and Accuracy: Defining Precision To keep things steady in round-the-clock warehouse moves or fast travel, gears need to get built and checked against tight global rules. ISO 1328 Grade 4 and 5 Precision Accuracy levels set the allowed slip in tooth shape, spacing, and slant: Grade 4/5: This sets the bar for robotics and EVs. Reaching Grade 4 keeps the shape slips under 4 µm, key for runs over 10,000 RPM. DD Gear Commitment: We use the newest Reishauer and Klingelnberg CNC grinders to aim for ISO Grade 4 accuracy or better for all custom jobs. Minimizing Transmission Error (TE) and Backlash Transmission error—the gap between the planned and real spot of a gear in turn—causes most gear hum. High-End Grinding: Getting a surface smooth to Ra 0.4 μm or finer helps meet tough NVH needs in passenger EVs. Backlash Control: In robotic joints, custom play gaps get held tight (often in a few arc-minutes) to stop loose moves, which can lead to robot shake and spot mistakes. Technical rules for round gears are kept and refreshed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), offering a shared way to talk about gear quality. Data-Driven Case Studies: Optimizing Performance Ideas turn real in actual use. Here come samples of how custom work at DD Gear fixed tough running issues. Case Study 1: Reducing NVH in a Passenger EV Reducer A new-energy vehicle maker dealt with a sharp whine at road speeds (80–110 km/h). The Problem: Regular helical gears in the two-stage reducer had built up slips that stirred up steady noise. The Solution: DD Gear supplied a custom helical gear set with 18CrNiMo7-6 steel and fine-tuned small shapes (crowning and end-relief). Result: A big drop in steady noise and better mesh work, helping cut energy use (kWh/100 km). Case Study 2: Stabilizing a Bipedal Humanoid Robot A robotics firm fought with balance because its joint drives had too much mechanical give. The Problem: Big play in standard planetary gearheads caused sway in steps. The Solution: We worked together on custom small-module planetary gears (sun, planet, and ring) with sub-micron tooth accuracy. Result: The joint loose motion dropped a lot, leading to even paths and steadier balance hold. Conclusion: The DD Gear Advantage Picking the best custom precision gear pays off over time in setup steadiness. While basic gears might work for plain belts, the calls of the “Future of Motion”—robotics, EVs, and smart automation—need a focused way. DD Gear brings high-precision gear answers fitted to your case, motor, and sound aims. We give: 15+ Years of Experience: Counted on by world makers and Fortune 500 firms. Fast Iteration: High-precision custom samples usually ship in 2–3 weeks. Certified Quality: Plants hold ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 marks to deliver steady top answers. FAQ Q: What is the primary cause of gear noise at high speeds? A: Small slips in tooth shapes, called transmission error, make teeth hit instead of slide easily, leading to a sharp hum. Q: Why are small-module gears necessary for modern robotics? A: Small-module gears (0.2–0.8 mm) let builders fit huge torque and big drop ratios into tight areas, like robot arms or humanoid joints. Q: Does DD Gear support prototyping for new designs? A: Yes. We handle small start orders and usually send custom samples in 2–3 weeks. Q: Which industries use DD Gear products? A: Our precision gears show up in humanoid robots, EV drivetrains, AGVs, medical imaging equipment, and high-speed CNC machinery.
Custom Gears: Key Industries Driving Demand for Tailored Solutions
In the quickly changing field of industrial automation, machines today must run faster, handle bigger loads, and fit into tighter spaces. Inside these complex systems, the behavior of one precision cylindrical gear can decide if everything works quietly and accurately or ends in a serious breakdown. When regular off-the-shelf parts fail to meet the strict needs for cutting noise, controlling vibration, and lasting many years, only custom precision gears tailored for specific applications provide a reliable solution. provide a reliable answer. The Rise of Customized Engineering in High-Performance Sectors Standard gears often reach their limits in special applications. This simple fact pushes the strong demand for custom precision helical gears and similar tailored parts. DD Gear concentrates on build-to-print custom projects. We produce precision small-module gears made for particular torque levels, limited housing room, and set noise limits. Through custom engineering, builders can adjust tooth flank features—such as crowning and tip relief—for smoother power transfer and much longer gear life. Electric Vehicles (EV): Precision for Efficiency and Silent Operation The electric vehicle sector drives the growing need for high-precision gears that enhance electric vehicle drivetrain gears, improving drivetrain efficiency while reducing noise.Electric cars have no loud engine sound to hide problems, so gear whine and tonal noises stand out clearly to drivers and passengers. Overcoming Noise, Vibration, and Harshness (NVH) Motors in electric vehicle drivetrains frequently turn at 12,000–18,000 RPM. Under those conditions, a tooth profile error of just a few microns can create a sharp whine. Custom helical gears solve this problem well. Their angled teeth mesh step by step, spreading the load and cutting vibration a lot. Customized EV Transmission Components DD Gear offers several custom parts for EV drivetrains: Input Shafts: Built for steady operation at high speeds, these connect the electric motor to the gearbox first. Main Reduction Gears: They change high motor torque into torque at the wheels, affecting fast starts and overall battery use. Parking End Gears: Custom-made to resist strong shocks while keeping exact tooth spacing for safe locking. Intermediate Drive Shafts: Shaped to manage sudden torque spikes and stay in line to lower torque steer. By grinding custom gears aim to upgrade ISO levels, EV builders can gain up to 1.2% better drivetrain efficiency. For details on worldwide gear standards, visit the ISO. Robotics and Humanoid Joints: Zero-Backlash and Compact Power For robotics and humanoid joints, zero-backlash gears for robotics are required, providing high-precision planetary gears that ensure minimal play and consistent torque density in compact spaces. Achieving Micron-Level Positioning Accuracy A robot arm often places parts with repeatability of ±0.02 mm. Any play or backlash in the gear train causes obvious wobbles and path mistakes. Custom zero-backlash gears are necessary for steady control in joints like hips, knees, and elbows. Customized Solutions for Robotic Actuators To reach large reduction ratios up to 320:1 in a space the size of a coffee cup, custom gear sets are required. Harmonic Reducer Components: DD Gear supplies custom flexsplines and circular splines for big single-stage reductions. Planetary Gear Sets: These work as servo gearheads, providing high torque density and low backlash with custom sun, planet, and ring gear shapes. Small-module gears from 0.2 mm to 0.8 mm allow these ratios to fit inside slim actuator housings. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and Logistics: 24/7 Durability In nonstop warehouse operations, AGVs and Autonomous Mobile Robots go through tough daily routines. Handling Frequent Start-Stop Cycles and Shock Loads Custom gear sets for AGVs are built to endure shock loads of 400–600 Nm, offering durable gears for high-speed applications and ensuring reliability during high-frequency operations in logistics. Standard gears usually develop early pitting and surface damage in such hard use. Customized AGV Drivetrain Systems DD Gear makes custom AGV gears from case-hardened alloy steels like 18CrNiMo7-6 or 20MnCr5. The custom heat treatment forms a hard outer layer at 58–62 HRC to resist wear. The core stays tougher at 35–45 HRC to handle sudden impacts. This setup delivers three to five years between maintenance stops, even in busy logistics areas. Machine Equipment and Industrial Automation For precision gears for CNC machines, custom helical gears for power tools and industrial automation gear solutions ensure high-speed timing and minimal backlash, improving manufacturing process efficiency. High-Speed Stability in CNC Machining CNC spindles and feed gearboxes require very low backlash and high stiffness for fine surface finishes. Switching from standard spur gears to custom small-module helical gears improves gear life by 30% and significantly reduces operational noise. Coordination in Packaging and Textile Machinery Packaging Machinery: Custom gears keep film feeds, sealing jaws, and filling steps in perfect sync in nonstop plants. Textile Machinery: Precision custom gears time multiple rollers and spindles to stop yarn breaks or fabric marks. Many engineers look to the AGMA for accepted gear design and accuracy rules. Power Tools and Specialized Applications Custom high-torque gear designs are essential in handheld tools and building systems, where compact spaces and high performance are required. Compact Strength for Handheld Drills and Grinders Custom gearheads for power tools, including spiral bevel and helical stages, provide high torque while reducing vibration for improved user comfort. Safety and Performance in Automatic Doors and E-Motorcycles Automatic Doors: Custom worm and helical stages give strong start torque and self-locking for safety in crowded buildings. E-Motorcycles: Custom planetary hub-motor sets or mid-drive helical stages deal with high electric motor speeds for smooth city rides. The DD Gear Advantage: Mastering Precision Gearing DD Gear is a focused producer of custom precision gears for high-performance applications with more than 15 years of experience. We work only on build-to-print jobs for worldwide OEMs in robotics, EV, and automation areas. Manufacturing Excellence: We use modern Reishauer and Klingelnberg CNC grinders to aim for ISO Grade 4 accuracy or better. Quality Control: Every gear gets full checks on CNC measuring machines and noise chamber tests before shipping. Fast Iteration: We aid quick product cycles by delivering high-precision prototypes in 2–3 weeks. Conclusion The move to faster speeds, smaller spaces, and quieter running has left standard gears behind in many advanced fields. From custom precision gears for electric vehicles to small-module gears for robotics and custom gear sets for AGVs, these tailored solutions are central to modern engineering performance. By matching tooth design to exact load, speed, and setting demands, custom gear parts from DD Gear keep future machines running smoothly and dependably. FAQ Q: What is the primary cause of gear noise at high speeds? A: Gear noise usually comes from transmission error caused by tiny tooth flank shape flaws. At speeds over 10,000 RPM, deviations of a few microns can produce a clear high-pitched whine. Q: Why are small-module gears required for modern robotics and EVs? A: Small-module gears help designers fit large torque and high reduction ratios into very small spaces, stopping the gearbox from taking too much room in the machine. Q: What level of accuracy can DD Gear guarantee for customized projects? A: For critical/high-performance applications, we can achieve up to ISO 1328 Grade 4–5 accuracy, verified on CNC gear measuring machines, according to each project’s specification. Q: Does DD Gear support small-volume customized orders for prototypes? A: Yes. We accept flexible small quantities and can usually ship high-precision custom prototypes within 2–3 weeks.
Why Precision Gear Racks Are Essential for Optimal Performance
In today’s fast-paced world of industrial gear systems and automation, small measurements often decide if a system runs at its best or breaks down. Electric motors commonly hit speeds from 12,000 to 18,000 rpm now. This creates a strong need for parts that turn that power into exact straight-line movement. Picture a robot arm stopping precisely or a warehouse cart pulling heavy loads. The basic mechanical parts underneath control how well everything works. At DD Gear, we know that machines today pack tighter and run quicker than before. High accuracy forms the key to dependable operation. The Evolution of Linear Motion in Industrial Automation The drive for quicker tasks and tight control has changed how people think about linear drive systems and gear rack drives. Older setups often had trouble with noise and wear when run hard. Current systems, though, need accuracy levels that cut down on costly repairs and lost power. Small-Module Precision: Factories and warehouses today demand precision gear sets that take heavier loads in smaller spaces. This calls for top-quality small-module precision gears. High-Density Operation: Tight drives in robot joints or CNC paths may require big speed drops inside areas just 80 mm across. Heat Management: Constant fast running builds friction. Oil in a electric vehicle gearbox can reach 120 °C quickly, so parts must handle hot conditions well. Core Mechanisms: Why Precision Racks Define Performance Straight motion results come down to how the gear pinion and gear rack work together. Poor control at this spot leads to transmission error (TE). That error then causes wider problems across the machine. Minimizing Transmission Error and NVH Fast automated setups react strongly to tiny gear tooth shape differences. Flaws just microns large can produce clear noise, vibration, and rough feel (NVH). Gradual Engagement: Helical gears mesh bit by bit to spread force. Precision straight parts follow the same idea to reduce noise and shaking a lot. Micro-Geometry Fixes: Fine grinding adds small adjustments to tooth edges, like tip relief, crowning, and root easing. These keep contact steady even when the shafts flex under torque around 300–400 Nm. Surface Finish: Reaching Ra 0.4 μm or better matters for tough NVH rules in electric cars and automation work. Controlling and Eliminating Backlash For robot joints or CNC gear drives, no backlash is vital to keep positioning the same every time and motion steady. Repeatable Positioning: A robot arm placing a screw within 10 microns has no room for loose play. Torsional Stiffness: Quality parts fight twisting. This holds joints solid as loads shift and stops the wobble common in cheaper drives. Lost Motion: Cutting lost motion means control signals reach the end without getting stuck in mechanical slack. Material Science and Durability Standards The toughness of a linear gear system rests on metal quality and careful heat treating. A part that wears out after months of nonstop use creates risks that factories avoid. For more on how strong materials affect part life, look at the materials from Gleason, a top name in gear studies. Case-Hardened Alloy Steels for 24/7 Duty To handle repeated starts and stops plus big shocks (like 400–600 Nm at the gear wheel), special metals are needed. 18CrNiMo7-6 Alloy: Makers choose this steel for heavy jobs. It gives a hard outside (62–64 HRC) against wear and a flexible core for impacts. Carburizing Consistency: Good control keeps case depth steady within 0.05 mm. This can stretch a part of life from one year to three or five. Fatigue Resistance: High-grade hardened steels often add 25–35% to service time before wear shows up. Achieving ISO Grade 4 Accuracy Accuracy means real measured standards, not just words. Reaching ISO 1328 Grade 4 gear accuracy requires very close limits. Profile Tolerance: Shape errors must stay below 4 µm. Lead and Pitch: Lead errors under 6 µm and pitch under 5 µm support speeds over 10,000 rpm. Efficiency Gains: Lifting a part from Grade 7-8 to 4-5 can raise efficiency by 0.6–1.2%. Over big operations, this saves noticeable energy. Application Scenarios: Where Precision is Non-Negotiable Accuracy needs change by field, but in critical work, it decides the final quality. You can find more engineering rules and standards for these setups at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). High-Speed CNC Machinery and Feed Systems CNC lathes and machining centers use precision gear racks for the spindle and feed boxes. Any mistake shows up as a poor surface finish or misaligned patterns. Positioning Accuracy: Today’s CNC tools need repeat placement around ±0.02 mm. Reducing Stoppages: Fine helical setups can cut gearbox breakdowns by up to 50%. Robotics and Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) AGV precision gear systems in busy warehouses face tough daily runs. They start and stop thousands of times per shift. Shock Load Management: These carts pull 1–2 tons and take sudden jolts that would ruin standard parts. Torque Density: Planetary and special straight stages often join to pack high turning force into small spaces, sometimes the size of a coffee cup. The DD Gear Advantage: Excellence in Customized Engineering At DD Gear, we avoid general solutions. We build custom precision gear racks focused on the exact noise, speed, and torque needs of our customers. Customized Design: We make parts to exact drawings with no off-the-shelf items. This fits your motor and housing just right. Fast Prototyping: Our staff can draw, build samples, and send custom test pieces in 2–3 weeks for quick checks on new ideas. Global Standards: Sites follow ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 rules. For critical/high-performance applications, we can achieve up to ISO 1328 Grade 4–5 accuracy using modern Höfler and Klingelnberg CNC grinders. Conclusion Do you need precision gear racks? It depends on your goals. If your setup calls for quiet running at 15,000 rpm, movement correct to a few microns, or strength for years of constant work, high accuracy is the practical path. Through custom building and top material choices, makers create bases for automated machines that do more than work – they lead the field. For broader applications beyond automation, PairGears supplies reliable gear solutions for agriculture, trucks, and construction machinery worldwide. FAQ Q: What is the main cause of noise in high-speed gear rack systems? A: The primary cause is transmission error (TE) resulting from minute shape deviations on the tooth flank. Even deviations of a few microns can cause significant whine at high speeds. Q: Why does DD Gear emphasize customized gear racks manufacturing over stock parts? A: Because high-performance systems for EVs, robots, and AGVs have unique constraints regarding space, torque, and NVH. Customized solutions ensure every micron of accuracy is optimized for the specific application. Q: What materials are best for high-cycle industrial environments? A: We typically use case-hardened alloy steels like 18CrNiMo7-6. These provide a hard exterior (62–64 HRC) to fight wear and a tough interior to absorb shock loads. Q: How does ISO Grade 4 accuracy affect energy efficiency? A: Moving from Grade 7-8 to Grade 4 can improve efficiency by up to 1.2%, which translates into more range for EVs or lower electricity costs for automated factories.
Choosing the Best Materials for Custom Gears
In the demanding field of industrial automation and electric vehicle drivetrains, a precision gear does much more than transfer power. It forms the basic building block for turning motion smoothly. Electric motors often run at input speeds of 12,000 to 18,000 rpm. This puts huge stress on high-torque gears. At such high rates, even a slight material weakness or wrong metal pick can cause quick wear, loud noise, or total breakdown. Good gear design starts with the right metal choices. The material decides how well a gear handles bending stress at the tooth base and pressure stress along the contact line. For a company like DD Gear, reaching top results comes from picking alloys and heat treatments that fit the exact torque, speed, and working conditions of each job. The Science of Metallurgy in Precision Gearing Picking the correct material is about finding the right mix for custom gears, not just going for the hardest one. A precision gear needs a tough outer layer to fight constant rubbing. Yet the inside must stay flexible enough to take sudden jolts without breaking. Understanding Case-Hardening Dynamics Many heavy-use high-torque gears rely on case-hardening alloy steels. These create two different layers in the metal. The Hardened Case: Methods like carburizing and quenching push the surface hardness to 60–64 HRC. This outer skin stands up to wear and stops pitting during nonstop running. The Tough Core: The surface stays very hard, but the center holds at around 35–45 HRC. This lets the precision gear absorb big shocks, like the 400–600 Nm forces in Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) when they stop fast. The Impact of Grain Structure on Fatigue Life Metal quality begins early, when the blank is shaped. High-end custom precision gears often start as forged pieces instead of plain bar metal. Forging aligns the grain flow along the tooth shape. This boosts strength against repeated stress a great deal. For more details on how metal fatigue shortens part life, look at the articles from Machine Design. They cover alloy behavior in depth. High-Performance Alloy Steels: A Comparative Overview Each job calls for its own gear material makeup. The table below lists the main steels used in custom precision gear work: Material Grade Primary Characteristics Common Applications 18CrNiMo7-6 High load capacity, excellent core toughness, and high nickel content. EV main reduction gears, high-torque planetary stages. 20MnCr5 Economical, good carburizing properties, stable heat treat. Robotic joint gears, AGV drive units. SCM415/ SCM420 High wear resistance, good for small-module precision. E-motorcycle reducers, power tool gearheads. 17CrNiMo6 Similar to 18CrNiMo, it is designed for extreme durability. Heavy-duty industrial automation, e-axles. Stainless Steel Corrosion resistance, non-magnetic options available. Medical imaging equipment, surgical robotics. Application-Specific Material Strategies A custom method means matching the metal to how the machine runs. Electric Vehicles and NVH Sensitivity In electric vehicle gearboxes, there is no engine noise to cover drivetrain gear sounds. Whine from the drivetrain stands out. Studies from places like Gleason show that transmission error causes most of the steady tones. 18CrNiMo7-6 stands out as the top choice. It allows fine grinding after heat treating to reach ISO 1328 Grade 4 accuracy. This steel works well with thin oils that raise efficiency. Those oils need very smooth tooth faces (Ra 0.4 μm or better) to stop tiny surface damage. Robotics and Torsional Stiffness Robot joints demand no play and strong resistance to twisting. This keeps the end tool from drifting. Small-module precision gears (usually 0.3–0.8 module) in these joints use metals that fight bending under shifting loads. Custom planetary gears for robots often pick 20MnCr5 for torsional stiffness. It helps the gears stay stiff and repeat positions over millions of moves. Medical Equipment and Non-Magnetic Requirements Devices like MRI machines need non-magnetic gears that do not affect magnetic fields. Custom work for these areas turns to non-magnetic metals such as aluminum bronze, brass, or austenitic stainless steels. These metals are softer than alloy steels. Special coatings like nitriding add wear protection without the shape changes from hot quenching. Advanced Treatments: Beyond the Base Metal The starting metal is important, but the final steps shape how well custom precision gears perform. Nitriding vs. Carburizing Carburizing: Best for heavy loads in AGVs and EVs. It builds deep, hard layers (up to 1.2 mm) for shock handling. Nitriding: Better for fine accuracy jobs where shape change must stay low. Lower heat keeps tolerances tight without the bending seen in usual quenching. Surface Finishing for Efficiency Switching to ground and polished gear teeth can lift drivetrain efficiency by 0.6% to 1.2%. For a group of electric delivery vans, that small boost adds real distance on each battery charge. The DD Gear Advantage: Excellence in Customized Engineering At DD Gear, we have built over 15 years of skill in making small, high-accuracy gears. We know every tiny measurement and metal decision counts. Customized Build-to-Print: We avoid stock items. Each precision gear set comes from your drawings, run cycles, and noise goals. Global Standards: Our shops follow IATF 16949 and ISO 9001 rules. For critical applications, DD Gear can achieve up to ISO 1328 Grade 4–5 accuracy, verified on Klingelnberg P26/P40 gear measuring machines. Rapid Validation: We help new companies and big makers with quick custom samples, often sent in 2–3 weeks. Advanced Inspection: All gears go through full checks on Klingelnberg P26 or P40 machines. This confirms a steady tooth shape and lead. Conclusion Do all gears need top-grade materials? Not always. But in fast, crowded systems where downtime costs big, the metal forms the base of everything. With custom gear alloys and careful heat processes, builders create machines that run quieter, last longer, and move with the exactness today’s work requires. FAQ Q: Why is 18CrNiMo7-6 preferred for EV gearboxes? A: This alloy provides an exceptional balance of surface hardness and core toughness, which is necessary to handle the high input speeds (up to 18,000 rpm) and high torque of electric motors while maintaining low noise levels. Q: How does DD Gear ensure the accuracy of customized gear materials? A: For critical applications, DD Gear can achieve up to ISO 1328 Grade 4–5 accuracy, verified on Klingelnberg P26/P40 gear measuring machines. Inspection plans combine 100% checks on key features with batch-level validation according to each project’s risk and quality requirements. Q: Can you provide customized gears in non-magnetic materials? A: Yes. For medical and MRI applications, we offer customized solutions using aluminum bronze, brass, and austenitic stainless steels to ensure zero magnetic interference. Q: What is the typical lead time for customized prototypes? A: We pride ourselves on fast reaction times, generally delivering customized prototype gears within 2–3 weeks to help you validate your designs quickly.
Why Gears Are the Hidden Force Behind Electric Motor Performance
Modern machines have seen major changes. Electric vehicles pick up speed without much noise, while surgical robots achieve control at the micron level. Compact, high-speed electric motors power this widespread shift. Many of these motors turn above 15,000 rpm—often too fast for direct applications without the use of gear sets. Gear sets handle this gap as the quiet backbone. At DD Gear, the staff recognizes that motor capability depends heavily on the precision gears for electric motors that manage its force. Over 15 years in the business, the company delivers custom precision gear solutions that link raw electric power to reliable, strong movement. The Essential Synergy Between Motors and Gears Electric motor gear sets play an important role in the efficiency of electric motor setups. They adjust the quick, low-torque spin from the motor to match the needed speed and greater torque for the work. Growing fields demand this conversion in smaller and smaller spaces. The Shift to Small Module Precision Motors grow smaller yet stronger, driving sharp rises in demand for small module gears (often 0.3 to 0.8 module) in electric motor gear applications. These fine teeth pack big reduction ratios into units as compact as a mug. Torque Density: High-precision planetary gearsets offer solid torque in limited volume, fitting well for robot joint drives and AGV wheel hubs. Precision Imperative: Tiny teeth leave very little margin for error. A deviation of mere microns in tooth profile can cause loud howling or fast wear in high-speed electric motor gear reducers. Integration: Today’s designs frequently need combined gear-shaft parts to cut joining points and raise alignment in compact motor assemblies. Core Structural Dynamics Defining Performance Precision gear design is critical as basic gears differ from high-performing ones in fine shape details, especially for electric motor applications. Tooth Geometry and Engagement Mechanics Spur Gears: Straight teeth align with the shaft. They transfer power efficiently, reaching 94–99%, and create no side force, often suitable for budget applications at moderate speeds in tight spots. Helical Gears: Gear tooth geometry for motors plays a crucial role. Helical gears with slanted teeth contact step by step, which helps reduce Noise, Vibration, and Harshness (NVH) in high-speedhelical gear reducers for electric motors. Worm Gear Sets: Seen in auto doors or medical lifts, they supply large ratios up to 100:1 and hold position for safety. Micro-Geometry Modifications for Acoustic Excellence In low-noise electric setups, small tooth form errors may result in whines. Experienced builders rely on gear micro-geometry modifications and ISO standards for cylindrical gear quality grades to ensure low noise and smooth operation. Tip Relief and Crowning: These minor adjustments, usually microns in size, keep contact smooth as heat causes parts to grow. Lead Corrections: Such changes avoid load on tooth edges, sharing torque across the face for extended life in precision motor gear sets. Surface Finishing: Advanced grinding hits Ra 0.4 μm or smoother, cutting drag and lifting drivetrain output by up to 1.2%. Material Science and High-Cycle Durability Each tooth endures bending near the base and pressure on the working line with every cycle. Metals and processing are designed to withstand millions of turns. Advanced Metallurgy for High-Speed Applications High-speed gear metallurgy is crucial. Strong motor gears typically start as forged pieces of chosen alloy steels. 18CrNiMo7-6 & 20MnCr5: Case-hardening steels keep resilient centers under hard shells. SCM415 & SCM420: Used widely in electric bikes and tools, they resist surface fatigue well. Non-Magnetic Options: Medical scanners like MRI machines employ custom gears from aluminum bronze or austenitic stainless to prevent field disruption. Precision Heat Treatment and Case Hardening Precision heat treatment for gear performance typically aims for hard exteriors over tough interiors, ensuring durability and reliability in high-performance electric motor gear sets. Carburizing: Carbon builds in the outer layer before cooling for 58–62 HRC hardness. Controlled Case Depth: High-torque setups hold depths from 0.6 mm to 1.2 mm within 0.05 mm to fight sudden stress. Nitriding: For lighter, accurate stages, it adds hardness with little shape shift, keeping close tolerances in small module precision gears. Overcoming Next-Generation Operational Challenges High-performance gear designs are crucial as electric motors reach new uses, requiring solutions for power saving and sound control in electric motor gear systems. NVH Control in High-RPM Environments NVH control for electric motor gears becomes essential in EVs and household robots, where there’s no engine roar to hide gear sounds. High-Speed Input: Input parts maintain ISO Grade 4-5 while coping with up to 18,000 rpm. Dynamic Balancing: Shafts and rotors balance to G1.0 to stop shakes that harm bearings. Transmission Error (TE) Analysis: Lowering TE removes tonal noises in current gearboxes. Range Maximization Through Efficiency Power saved in gears adds real distance for battery rides or longer runs for AGVs. Grinding vs. Hobbing: Gear efficiency in electric motors is boosted by grinding vs. hobbing. Polished Grade 4-5 gears generally reduce drag compared to hobbed Grade 7-8. Lubrication Optimization: Tooth surfaces match thin oils to cut loss further. Builders often refer to AGMA standards for strength and safety in high-performance electric motor gears. Customized Solutions for Motor Systems DD Gear focuses on custom gear solutions for electric motors, designed to match torque patterns, sound limits, and size rules. The team serves as design partners. Integrated Power Stages: Custom planetary components—sun gears, planet carriers, ring gears—suit robot actuators and AGV drives. Specialized Components: Precision rotor shafts for traction or parking lock gears for EV safety get fitted per task. Fast Iteration: Prototype gear sets arrive in 2–3 weeks to keep pace with quick changes. For humanoid robots, heavy cutters, or quiet buses, small module precision pushes electric motor capability to its best. FAQ Q: What gear accuracy levels can DD Gear achieve? A: We aim to achieve ISO 1328 Grade 4–5 accuracy for high-performance applications, using advanced Klingelnberg and Reishauer grinding and inspection machines. Q: Does DD Gear support small-volume customized orders? A: Yes. We offer flexible MOQs and provide fast prototyping services, with most prototype sets shipping within 2–3 weeks. Q: Why is small module gear design for electric motors essential for modern drivetrains and robotic systems? A: Small modules (0.3–0.8) allow for high reduction ratios in very compact spaces, which is essential for modern, lightweight EV drivetrains and robotic joints. Q: Which industries use your precision gears? A: Our parts are critical components in electric vehicles, humanoid and industrial robots, warehouse AGVs, medical imaging equipment, and professional power tools.
Key Design Factors That Define High-Precision Small Module Gears
In today’s engineering world, equipment runs quicker, delivers more power, and takes up far less room. A surgical robot might move with accuracy down to microns, or an electric vehicle might glide along highways without much sound. At the center of such systems often sits a high-precision small module gear set, sometimes smaller than a coin. Reaching this kind of capability demands careful knowledge of customized high-precision small module gears solutions, where even minor mistakes can lead to significant issues. DD Gear has focused on these parts for more than 15 years. The company supplies tailored small module gear solutions that support advanced automated systems. Fundamental Dynamics of Small Module Gear Design The module describes tooth size on a gear, which plays a critical role in small module gear accuracy. Smaller modules mean finer teeth, which pack large speed reductions into tight spaces. Fine teeth, however, leave very limited room for errors. An error of just several microns in shape can cause loud noise, fast wear, or complete breakdown. Load Capacity and Material Science Each gear tooth faces heavy bending at the base and pressure along the contact line with every turn. Picking suitable metal forms the starting point for a long service life. Alloy Selection: Many high-strength small module gearsstart from forged bars of alloys such as 18CrNiMo7-6 or 20MnCr5. The Carburizing Process: Gears go through carburizing to build a hard outer layer, usually 58–62 HRC, while keeping a tougher inner core at 35–45 HRC. This mix handles wear and sudden shocks. Case Depth Consistency: In custom small module gear projects, holding case depth within 0.05 mm helps parts last through constant running. Tooth Profile and Engagement Mechanics How teeth touch during rotation sets the smoothness and sound level of the machine. Builders commonly choose between two main types of cylindrical gears. Spur Gears: Straight teeth run parallel to the shaft. They transfer power efficiently, with an efficiency range typically between 94% and 99%, and are less expensive to manufacture. All teeth meet at once, though, which can produce a sharp noise and shaking at higher speeds. Helical Gears: Angled teeth allow gradual contact. This smooth shift cuts down Noise, Vibration, and Harshness (NVH) in high-precision helical small module gears. Many designers turn to the ISO for rules on cylindrical gear geometry and quality levels. Critical Factors for High-Precision Performance When rotation speeds pass 10,000 rpm, or positioning needs micron-level repeat, small shape differences turn into real troubles. High-precision small module gears follow stringent manufacturing and inspection guidelines to ensure reliable performance, with an aim to achieve micron-level precision when required. Accuracy Standards and Micro-Geometry Standard gears seldom meet the demands of robotics or electric drivetrains. ISO Grade 4-5 Accuracy: This calls for profile errors below 4 µm and helix variations under 6 µm. Micro-Geometry Modifications: Small changes like tip relief, crowning, and lead adjustments help keep quiet running as parts warm up. Composite Error Control: Overall composite deviation often stays below 10 µm to avoid whining sounds in fast gear sets. Manufacturing Excellence and Surface Finishing Gear quality depends on the tools and conditions used to finish it. Precision Grinding: Machines from Reishauer or Klingelnberg typicallyproduce surfaces smoother than Ra 0.4 μm, a hallmark of high-precision gear grinding. Temperature Control: Grinding rooms hold steady heat, since a shift of two degrees can alter helix angles on fine parts. Rigorous Inspection: Custom gears get checked on units like the Klingelnberg P40 to confirm they reach the required ISO or AGMA level. Application-Specific Design Requirements Various fields set different loads on gear pairs, calling for tailored small module precision gear designs. Electric Vehicles (EV) and NVH Control Electric motors run quietly, so any gear noise stands out inside the cabin. High-Speed Input: Motors commonly reach 12,000 to 18,000 rpm. Helical Mandate: Helical small module gears become necessary in main reducers for passenger comfort. Efficiency Gains: Moving from Grade 7-8 to polished Grade 4-5 can raise drivetrain output by 0.6-1.2%, adding real distance to battery range. Robotics and Zero-Backlash Imperatives Robot joints must return to the same spot each cycle, needing robotics precision gears with almost no play. Small Module Precision: Joints often use modules ranging from 0.3 to 0.8 to fit slim actuators. High Torsional Stiffness: Stiff, accurate tooth forms prevent wobble during moves. AGVs and Industrial Shock Durability Automated Guided Vehicles in warehouses carry loads of 1–2 tons through repeated starts and stops, relying on shock-resistant small module gears for durability. Shock Load Management: Gears handle sudden torques of 300–600 Nm without surface damage or breaks. Planetary Combinations: Many drives pair a planetary stage for compact power with a helical stage for even delivery. Builders frequently check AGMA guides for tooth strength and life calculations in high-precision small module gears. The Value of Customized Precision Solutions DD Gear does not sell standard stock items. Instead, the company specializes in custom gear solutions for robotics and other advanced systems. The company handles build-to-print custom projects fitted to exact space and work cycles. This method matches every high-precision small module gear to its role. Engineering Partnership: Staff recommend alloys, heat treatments, and tooth changes early to extend part life. Rapid Prototyping: Custom small module gear samples usually arrive in 2–3 weeks to match fast project timelines. Advanced Metallurgy: Choices range from 18CrNiMo7-6 for heavy electric axles to non-magnetic stainless for medical scanners. For new surgical robots, fast electric reducers, or tough warehouse drives, focusing on small module precision helps maintain quieter and more stable systems over time. FAQ Q: What gear accuracy levels can DD Gear guarantee? A: For critical/high-performance applications, we can achieve up to ISO 1328 Grade 4–5 accuracy, verified on CNC gear measuring machines, according to each project’s specification. Q: Do you support small-volume customized orders and prototyping? A: Yes, we offer flexible MOQs and can deliver high-precision small module gear prototyping within 2–3 weeks. Q: Which materials are most common for high-load small module gears? A: We typically use case-hardening alloy steels such as 18CrNiMo7-6 and 20MnCr5 to achieve a high surface hardness of 60+ HRC with a tough core. Q: Why are helical gears preferred over spur gears in high-speed applications? A: Helical gears offer gradual tooth engagement, which significantly reduces vibration and noise compared to the sudden contact of spur gear teeth.
LOVE TO HEAR FROM YOU GET IN TOUCH!
Please fill out the form below and we will get back to you as soon as possible.